How to read electricity and natural gas bills
It is always a good idea to check utility bills on a regular basis, even if automatic withdrawal is enabled to ensure charges are accurate.
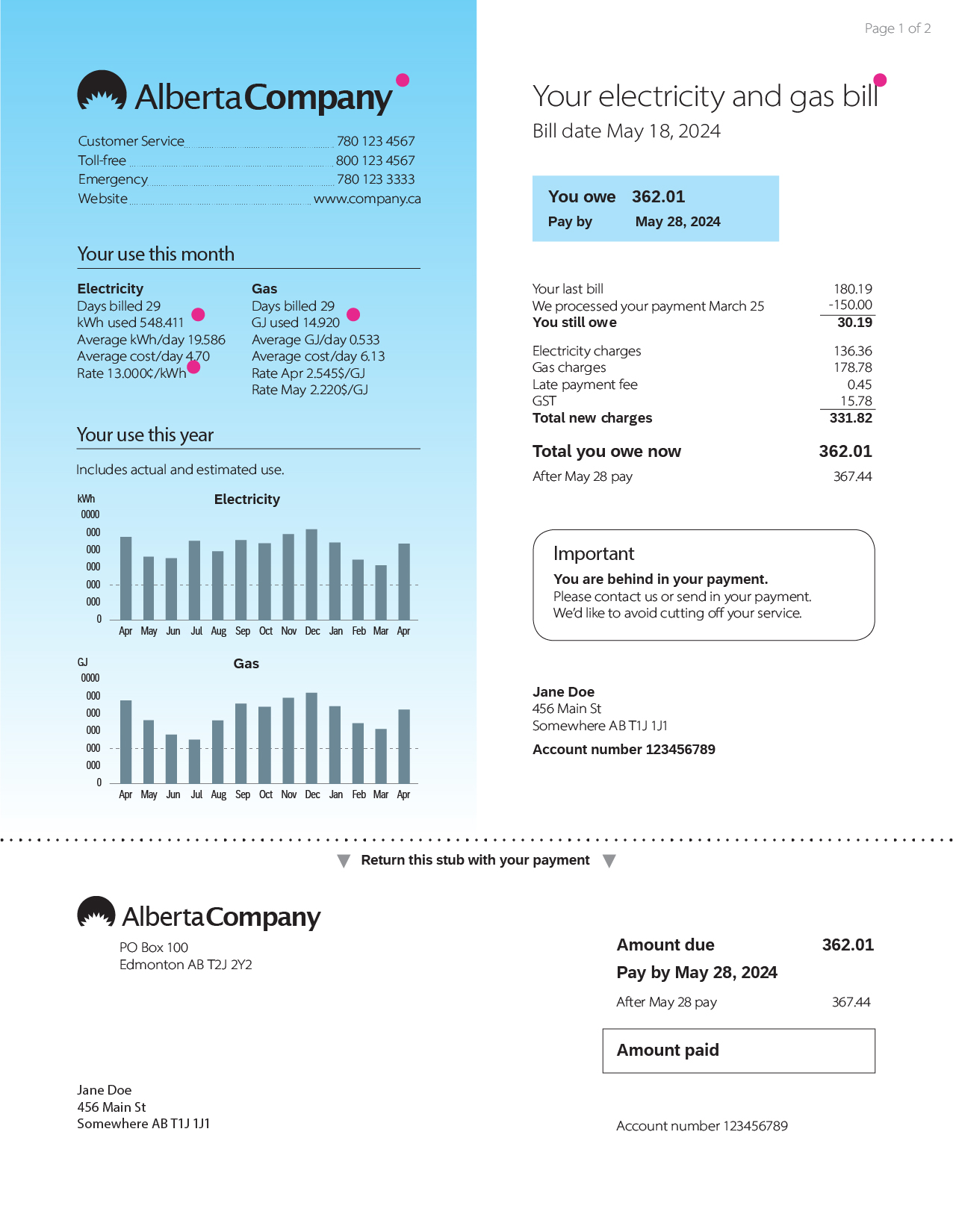
Please click on the image to learn about various line items and charges on electricity or natural gas bills.
There are two kinds of retailers. Default retailers set their rate using a formula approved by the Alberta Utilities Commission. Competitive retailers set their rate independently. Consumers can choose their retailer.

Transmission: Transmitting electricity or moving gas over long distances from the source to the local area.
Distribution: Transmitting electricity or moving gas within your area, usually within the city or town.
Transmission: Transmitting electricity or moving gas over long distances from the source to the local area.
Distribution: Transmitting electricity or moving gas within your area, usually within the city or town.
A short video guide to understanding utility bills
Charges on electricity and natural gas bills
Two main charges make up utility bills:
- The cost of energy consumed
- The cost of delivering this energy
Energy charges are based on how much electricity and natural gas was consumed during the billing period, while the cost of delivering the energy is largely fixed.
Delivery charges cover the cost of installing, operating, and maintaining the infrastructure that's used to transmit energy to homes, small businesses, and farms. For electricity, this infrastructure includes poles, wires and transformers. For natural gas, infrastructure includes pipes and compressor stations.
Delivery company rates are regulated by the Alberta Utilities Commission (AUC). The AUC holds rate hearings to ensure that consumers receive safe and reliable services at a reasonable cost.
According to Section 4 of the Natural Gas Billing Regulation and Section 4 of the Billing Regulation (electricity), an electricity or natural gas bill must show all credits or charges as separate line items.
Bill corrections
When there are errors in billing, retailers may need to issue a bill correction (sometimes called a cancel rebill).
A corrected bill displays all the original charges that were cancelled and the newly created charges. This means that these bills are often multiple pages long.
A corrected bill can occur for many reasons such as previous bills using estimated consumption, incorrect line items, and incorrect meter readings. This may result in a charge or a debit. If consumers need assistance paying a corrected bill, they can reach out to the retailer to make a payment arrangement.
Bill concerns
Retailers are the first point of contact if consumers receive incorrect bills. The contact information can be found on the utility bill.


